Understanding VLAN: Virtual Local Area Networks Explained
What is VLAN? A Comprehensive Guide to Virtual Local Area Networks
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) are a crucial component of modern networking, allowing organizations to segment their network for improved efficiency, security, and manageability. Understanding VLANs can help you optimize your network's performance and ensure that sensitive data remains secure.
What is a VLAN?
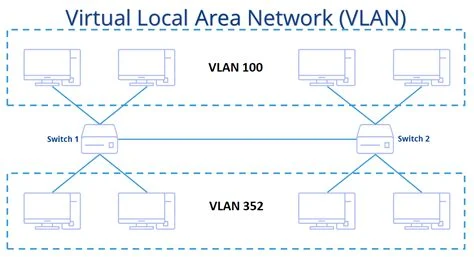
A VLAN, or Virtual Local Area Network, is a network configuration that allows you to segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. This segmentation enables you to group devices together based on factors like function, department, or application, regardless of their physical location. By doing so, VLANs can reduce network traffic, improve security, and simplify network management.
Benefits of Using VLANs
- Enhanced Security: VLANs can isolate sensitive data and restrict access to specific network segments. This prevents unauthorized users from accessing critical information and reduces the risk of data breaches.
- Improved Network Performance: By segmenting the network, VLANs can reduce broadcast traffic and prevent network congestion. This results in more efficient use of bandwidth and improved overall performance.
- Simplified Network Management: VLANs allow network administrators to manage different segments of the network more easily. Changes can be made to a single VLAN without affecting the entire network, making it easier to implement updates or troubleshoot issues.
- Flexible Network Design: VLANs provide the flexibility to group devices based on criteria other than physical location. This allows organizations to design their network in a way that best meets their operational needs.
How VLANs Work:
VLANs are created by configuring network switches to recognize and route traffic based on VLAN tags. Each VLAN is assigned a unique identifier, known as a VLAN ID. Devices within the same VLAN can communicate with each other as if they were on the same physical network, even if they are located on different switches.
Common Use Cases for VLANs
- Departmental Segmentation: Large organizations often use VLANs to segment their network by department. For example, the finance department might have its own VLAN to ensure that sensitive financial data is isolated from other parts of the network.
- Guest Networks: Many businesses use VLANs to create separate guest networks for visitors. This allows guests to access the internet without gaining access to the main corporate network, protecting internal resources.
- Voice and Video Traffic: VLANs can be used to prioritize voice and video traffic, ensuring that these services receive the necessary bandwidth for optimal performance. This is particularly important for businesses that rely on VoIP or video conferencing.
Setting Up a VLAN
- Determine Your VLAN Structure: Decide how you want to segment your network. Consider factors such as security, performance, and the specific needs of your organization.
- Configure Your Switches: Access your network switches' management interface and create VLANs by assigning VLAN IDs. Tag the appropriate ports to ensure that devices are correctly assigned to the desired VLAN.
- Test Your Configuration: After setting up your VLANs, test the configuration to ensure that devices within the same VLAN can communicate with each other and that traffic is correctly isolated between VLANs.
The Long-Term Impact of Using VLANs:
Implementing VLANs can have a significant positive impact on your network's security, performance, and manageability. By effectively segmenting your network, you can create a more efficient and secure environment that supports your organization's goals.



No comments